Calcular¶
Acerca de¶
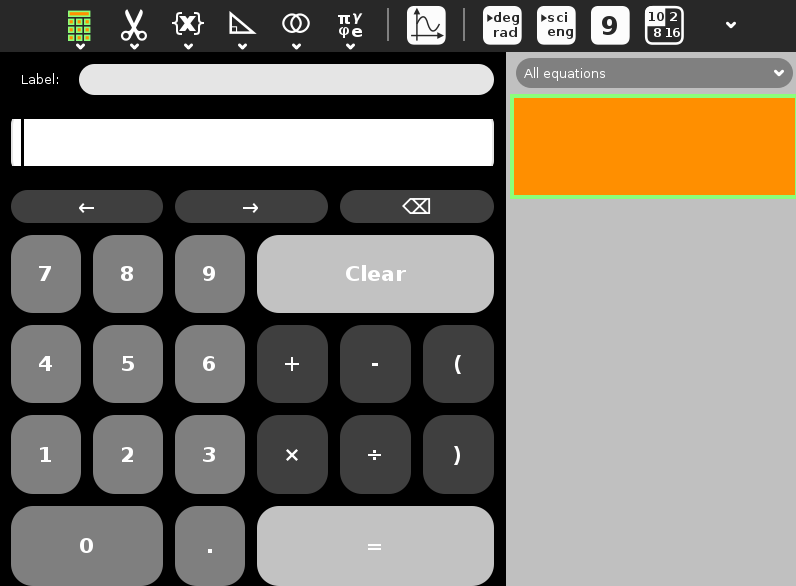
Utilizando Calcular¶
Para aquellos que han utilizado una calculadora científica, la mayoría de las funciones de Calcular serán muy familiares.
Las barras de herramientas son
Actividad, icono Calcular: Nombre de Sesión, descripción de la entrada en el Diario, colaborar
Editar, icono de las tijeras: Copiar, Pegar
Funciones, {x}: Cuadrado, Raíz cuadrada, recíproca, exponencial, potencia, logaritmo, factorial
Trigonometría, icono triángulo: seno, coseno, tangente, arcoseno, arcocoseno, arcotangente, seno hiperbólico, coseno hiperbólico, tangente hiperbólica
Booleanos, icono diagrama de Venn: y, o, =, =!
Constantes, letras griegas icono: pi, e, gamma, phi
Graficos: menú ofrece Ayuda
Grados/Radianes para la medida de ángulos
Notación Científico / Ingeniería
Número de dígitos a mostrar: 6, 9, 12, 15
Base: decimal, binaria, octal, hexadecimal
Salir
Obteniendo ayuda¶
Para ver una opción de ayuda para gráficas, entre el mandato
help(plot)
en la línea de entrada de texto.
La función de ayuda general es
help()
La lista de temas de ayuda está disponible con el comando
help(index)
incluyendo temas que no son compatibles en los menús. La ayuda no se proporciona para las constantes pi, e, gamma (Euler-Mascheroni constante) y phi (Golden Ratio), pero éstas se puede consultar en Internet. Al hacer clic en sus iconos inserta sus valores numéricos.
Functions in Calculate¶
These are the list of functions available in Calculate Activity:
- abs(x) - return absolute value of x, which means -x for x < 0
- acos(x) - return the arc cosine of x. This is the angle for which the cosine is x. Defined for -1 <= x < 1
- acosh(x) - return the arc hyperbolic cosine of x. This is the value y for which the hyperbolic cosine equals x.
- and(x, y) - logical and returns True if x and y are True, else returns False
- add(x, y) - return x + y
- asin(x) - return the arc sine of x. This is the angle for which the sine is x. Defined for -1 <= x <= 1
- asinh(x) - return the arc hyperbolic sine of x. This is the value y for which the hyperbolic sine equals x.
- atan(x) - return the arc tangent of x. This is the angle for which the tangent is x. Defined for all x
- atanh(x) - return the arc hyperbolic tangent of x. This is the value y for which the hyperbolic tangent equals x.
- b10bin(x) - interpret a number written in base 10 as binary, e.g.: b10bin(10111) = 23.
- ceil(x) - return the smallest integer larger than x.
- cos(x) - return the cosine of x. This is the x-coordinate on the unit circle at the angle x
- cosh(x) - return the hyperbolic cosine of x. Given by (exp(x) + exp(-x)) / 2
- div(x, y) - returns x/y where y!=0.
- gcd(a, b) - determine the greatest common denominator of a and b.For example, the biggest factor that is shared by the numbers 15 and 18 is 3.
- exp(x) - return the natural exponent of x. Given by e^x
- factorial(n) - return the factorial of n. Given by n * (n - 1) * (n - 2) * ... * 1
- factorize(x) - determine the prime factors that together form x. For examples: 15 = 3 * 5.
- floor(x) - return the largest integer smaller than x.
- inv(x) - return the inverse of x, which is 1 / x
- is_int(n) - determine whether n is an integer.
- is_prime(x) - Check if a number is a prime.For examples: is_prime(2).
- ln(x) - return the natural logarithm of x. This is the value for which the exponent exp() equals x. Defined for x >= 0.
- log10(x) - return the base 10 logarithm of x. This is the value y for which 10^y equals x. Defined for x >= 0.
- mod(x, y) - return the modulus of x with respect to y. This is the remainder after dividing x by y.
- mul(x, y) - return x * y
- negate(x) - return -x
- or(x, y) - logical or. Returns True if x or y is True, else returns False
- pow(x, y) - return x to the power y (x**y)
- rand_float() - return a random floating point number between 0.0 and 1.0
- rand_int([<maxval>]) - return a random integer between 0 and <maxval>.<maxval> is an optional argument and is set to 65535 by default.
- round(x) - return the integer nearest to x.
- shift_left(x, y) - shift x by y bits to the left (multiply by 2 per bit)
- shift_right(x, y) - shift x by y bits to the right (divide by 2 per bit)
- sin(x) - return the sine of x. This is the y-coordinate on the unit circle at the angle x
- sinh(x) - return the hyperbolic sine of x. Given by (exp(x) - exp(-x)) / 2
- sinc(x) - return the sinc of x. This is given by sin(x) / x.
- sqrt(x) - return the square root of x. This is the value for which the square equals x. Defined for x >= 0.
- square(x) - return x * x
- sub(x, y) - return x - y
- tan(x) - return the tangent of x. This is the slope of the line from the origin of the unit circle to the point on the unit circle defined by the angle x. Given by sin(x) / cos(x)
- tanh(x) - return the hyperbolic tangent of x. Given by sinh(x) / cosh(x)
- xor(x, y) - logical xor. Returns True if either x is True (and y is False) or y is True (and x is False), else returns False